
- WIFI SCANNER FOR MAC OS X LION HOW TO
- WIFI SCANNER FOR MAC OS X LION FOR MAC
- WIFI SCANNER FOR MAC OS X LION FREE
- WIFI SCANNER FOR MAC OS X LION WINDOWS
WIFI SCANNER FOR MAC OS X LION FOR MAC
They include a packet sniffer and a real-time performance monitoring tool, just to give two examples of some of the tools that make this humble wireless channel scanner for Mac so useful. Other wireless diagnostics Mac utilities included with the Wireless Diagnostics tool can be opened from the Window menu in the Wireless Diagnostics menu bar. You can use this file to learn even more information about your wireless network and other networks available in your local area, or you can send it to your network administrator and ask them to take a look at it. A new Wi-Fi scanner tool is in Mountain Lion’s. Once you’re there, push down the Option key (next to the CTRL key) on your keyboard and click the icon at the same time.
WIFI SCANNER FOR MAC OS X LION HOW TO
Now that you know how to run network diagnostics on Mac using the Wireless Diagnostics tool, you should also know that the tool automatically generates a WiFi diagnostics file and saves it in the folder /var/tmp. How To Access the Wi-Fi Scanner in Mac OS X Mavericks Step 1: Open Wireless Diagnostics Head up to your Mac’s menu bar and track down the WiFi icon. You can even scan directly to a USB memory drive without using a computer. This reliable performer makes it easy to scan to your smartphone, tablet or online storage account1 from your desktop or your mobile device.
WIFI SCANNER FOR MAC OS X LION WINDOWS
WIFI SCANNER FOR MAC OS X LION FREE
But without a wireless channel scanner, proper WiFi channel planning is impossible because you have no way of knowing which channels are busy and which are free from traffic. That’s why WiFi channel planning is so important, and why it should always precede every deployment of a WiFi network. While that may sound like a lot, only 3 of these channels are non-overlapping (1, 6, and 11), meaning they’re not affected by co-channel interference caused by adjacent channels. In North America, there are 11 channels available. WiFi networks (those that use the 2.4 GHz band) can also take advantage of multiple lines, or channels as they are called, when broadcasting data. That’s why busy highways tend to have multiple lines going both ways. When too many cars travel in the same line, the speed of traffic can slow down to a crawl and make traveling anything but enjoyable. Why? Because WiFi channels are sort of like the lines on the highway.
It’s paramount that you pick a channel that isn’t already occupied by several other nearby wireless networks. One available option lets you choose which WiFi channel the router should operate on. When you received your home router from your ISP, the chances are that you weren’t paying much attention to all configuration options available.
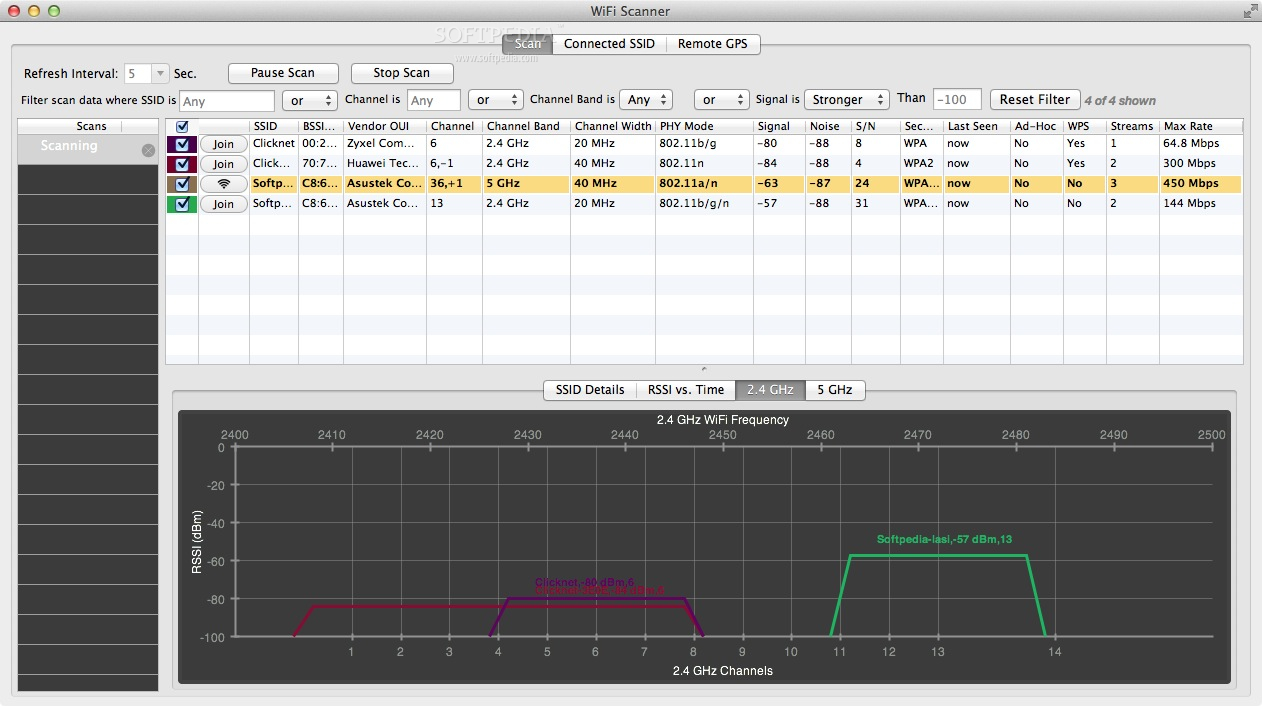
noise strength over those four waves Apple uses in its Wi-Fi menu.Īdditionally, by looking at what Channel (1-13) your base station is on, compared to your neighbors (or other base stations in your house), you can often find the least used channel in your area to improve reception. Some maneuvering of base stations can increase coverage to the outermost areas of your house, and it is much, much easier to see slight differences in numerical signal vs. It also has Active and Passive scan modes.įrom the window, you can see what networks are in your area and their strength. Comparable to third-party Wi-Fi stumbler tool iStumbler, the scan tool provides data for BSSID, band, protocol, channel, signal strength, security, and more. A new Wi-Fi scanner tool is in Mountain Lion’s refreshed Wi-Fi Diagnostics Utility, allowing users to easily discover Wi-Fi networks within range and view related data not available from Apple’s Wi-Fi menu bar item.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
